4.Sampling
4.1 Non-probability Sampling
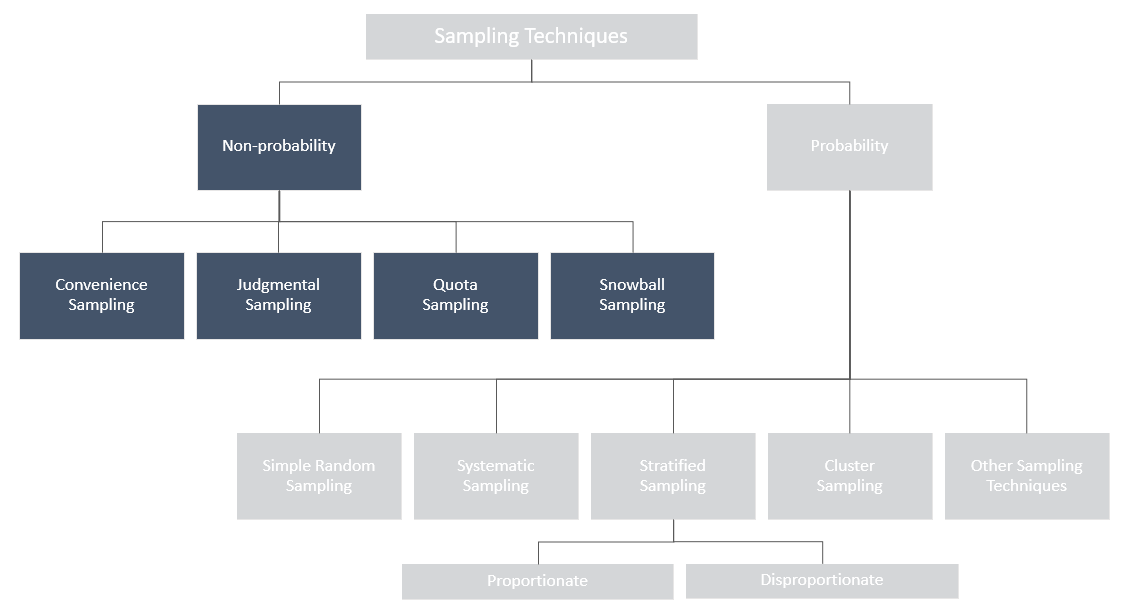
Convenience Sampling
 Convenience sampling attempts to obtain a sample of convenient respondents. Often, respondents are selected because they happen to be in the right place at right time.
Convenience sampling attempts to obtain a sample of convenient respondents. Often, respondents are selected because they happen to be in the right place at right time.
- students or members of social organizations
- mall intercept interviews without qualifying the respondents
- “people on the street” interviews
- tear-out questionnaires in magazines
Judgmental Sampling
 Judgmental sampling a form of convenience sampling in which the population elements are selected based on the judgement of the researcher
Judgmental sampling a form of convenience sampling in which the population elements are selected based on the judgement of the researcher
- test markets
- purchase engineers selected in industrial marketing research
- mothers as diaper “users”
Quota Sampling
Often used in online surveys
Quota sampling techniques develop control categories, or quotas, of population elements (e.g., sex, age, race, income, company size, turnover, etc.) so that the proportion of the elements possessing these characteristics in the sample reflects their distribution in the population.
The elements themselves are selected based on convenience or judgment. The only requirement, however, is that the elements selected fit the control characteristics (quota).

Snowball Sampling

An initial group of respondents is selected (usually) at random.
- After being interviewed, these respondents are asked to identify others who belong to the target population of interest.
- Subsequent respondents are selected based on the referrals.
Good for locating the desired characteristic in the population:
- reaching hard-to-reach respondents (e.g., government services, “food stamps”, drug users)
- estimating characteristics that are rare in the population
- identifying buyer-seller pairs in industrial research
